Have you ever questioned yourself about how plain drawings or no more than vectors appear to come to life on your screen? It is the wonder of Flash Animation, a revolutionary method that once swept the digital storytelling and internet interaction. This animation style initially required Adobe Flash (now renamed Adobe Animate) to create dynamic motion, smooth effects, and interesting visuals on websites, long before the emergence of modern platforms.
Flash was the creative backbone of early online animation due to its capabilities to produce scenes based on vectors and tweened motion, as well as interactive experiences. Although it has lost its online presence, which was almost 28 percent in 2011 and now stands at only 2.2 percent in 2021, its artistic impact remains evident in current cartoons, banner advertisements, and videos that explain concepts.
What is Flash Animation?
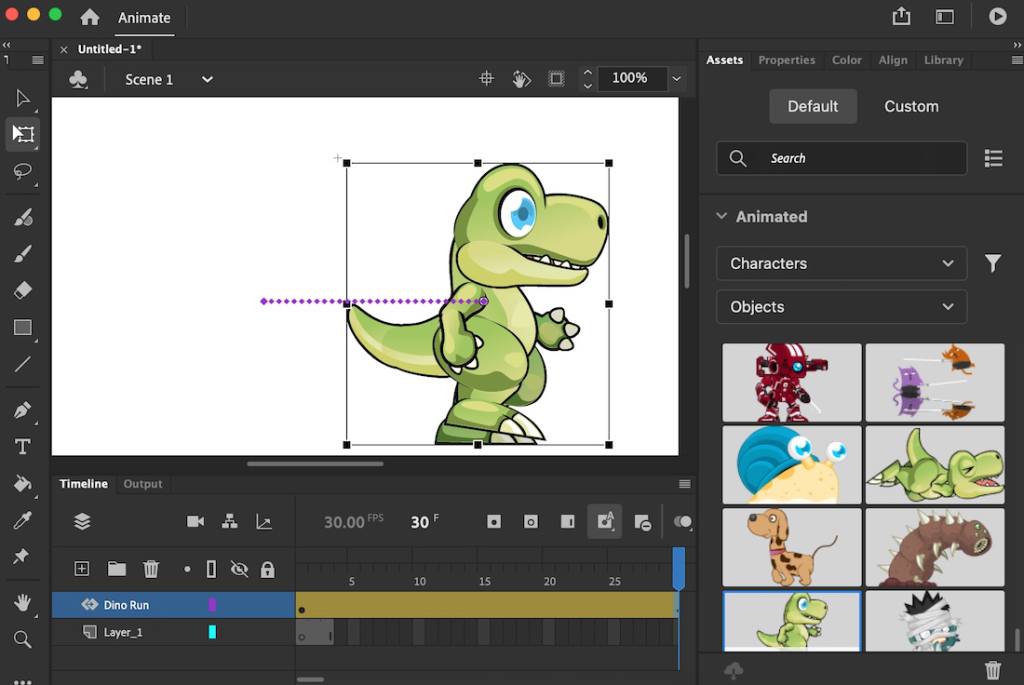
Flash animation is a form of digital animation that runs in the Adobe Flash (now renamed Adobe Animate) program or other programs compatible with Flash. Flash was also introduced in the late 1990s as one of the most important tools for creating animations, interactive elements, and web applications. The basic technology it had was vector graphics, which meant that the animation in it was not large in file size and could be scaled to a larger size without compromising quality. The popularity of these animations was also due to their lightweight nature, which made loading them easy and ideal for internet use, particularly in the early years of internet media.
Adobe Flash Animation Animate
A brief history of Flash animation should include its impact on the early web content, such as its contribution to changing websites by providing interactive banners, animated web series, and online games. Through its cognizance, we are able to value its heritage in web development and digital media.
1. Flash-Based Animation Tools
There are several Flash-based animation tools, but the most popular has been Adobe Flash (now renamed Adobe Animate).
2. 2D Flash Animation with Adobe Animate
Adobe Flash, now known as Adobe Animate, was originally created as a tool for creating 2D vector animations. Adobe has operated over the years by incorporating features that enable designers to add sound, video, and interactivity to animated videos, further broadening the application of Flash beyond graphics. Adobe Animate remains compatible with HTML5, but has been modernized with its Flash heritage. Although Adobe Animate is no longer available as a web-based plug-in, it remains a valuable tool for creating 2d Flash animation.
3. Other Flash Animation Tools
Such software tools also came into competition with Adobe Flash/Animate. SwishMax was a well-known Flash substitute that enabled developers to make animations in an easier interface, which was more user-friendly to novices. Toon Boom was also offering Flash-compatible exports to professional animators in need of increased functionality. Although Adobe Animate was adopted in the industry, these tools expanded the boundaries, allowing more creators to contribute to animated video creation.
Key Features of Flash Animation

As an animation tool in digital animation, Flash animation had several exclusive characteristics that set it apart from other tools and can be considered examples of Flash animation.
- Vector Graphics: The design of Flash animation as a vector-based allowed smooth scaling of animation, no matter the resolution, without the quality being compromised. This played a crucial role in ensuring visual clarity across varying screen sizes.
- Interactivity: It may also have interactive features such as clickable buttons, and was therefore appropriate for web-based games and interactive infographics.
- Timeline and Keyframe Animation: It brought a user-friendly timeline interface, which could be used to build frame-by-frame or tweened animations efficiently by the animator.
These attributes render Flash to be very diversified and can be used in many applications, such as web content, e-learning modules, and short-form video content.
Pros of Flash-Based Animation
It also contained considerable merits that made it widely adopted.
Small File Size
The vector graphics of Flash enabled it to use small file sizes, hence its animations are lightweight and can be loaded easily. This especially worked to the advantage of early internet users, who had no more than limited bandwidth, since it used less data compared to bitmaps. Its size in smaller files enabled creators to introduce animation to web pages without slowing the loading speed, thus becoming a web design standard.
Cross-Platform Compatibility
Among the largest promises that Flash offered was the idea of being cross-platform, meaning that the animations would run in most browsers and operating systems. Flash animations also made it possible to view on virtually any device with a Flash plug-in installed, unlike other formats that required various versions to be compatible. Flash was initially cross-platform, and that promise was the first to establish a model of multimedia accessibility. However, it was eventually prompted by mobile platforms, such as iOS, to support it on their own platforms.
Decline of Flash Animation
Flash’s popularity started to decline in the 2010s, despite its success, as new technologies emerged and security and performance issues were raised.
The Rise of HTML5
With the introduction of HTML5, web developers had a different platform for producing multimedia content without the use of a plug-in. CSS3 and JavaScript, in conjunction with HTML5, enabled animations that could be executed by browsers, thereby providing similar functionality with improved performance and reduced security risk. With the increased adoption of HTML5 by developers, Flash became superfluous, and web browsers slowly supported Flash.
Flash End-of-Life (EOL)
In December 2020, Adobe officially terminated Flash support, marking the end of the Flash/Animate-based animation era. Flash was terminated because it had security weaknesses, poor performance, and could be replaced by more efficient technologies such as HTML5. Large web browsers, such as Chrome, Firefox, and Safari, have ceased to support Flash, resulting in Flash-based web content becoming largely irrelevant.
Alternatives for Flash Animation.
Since Flash is no longer available, it has been replaced by other new standards such as HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScript, which enable animators and developers to develop dynamic content without using any kind of plug-in. The following are the top alternatives:
- HTML5: HTML5 is the new standard of web animation and interactivity. It is fully compatible with CSS3 and JavaScript, allowing developers to create intricate animations that can be executed in modern browsers without the need for any plug-in.
- CSS3: CSS3 has transitions, animations, and transformations, which enable designers to produce simple animations. CSS3 is best used in hover effects, button effects, and basic web elements.
- JavaScript: JavaScript can be used to control complex animations, giving developers the ability to develop complex animations, interactive objects, and responsive designs. Animations that have a fluid, responsive, and browser-compatible nature are simple to develop using libraries such as GreenSock (GSAP) and Anime.js.
Although Flash is no longer supported, it has left a legacy behind. Several tricks and concepts developed during the Flash era continue to influence the production of contemporary animation, and their contribution to making web-based animation popular has lasting effects on digital and online practices to this day.
The history of Flash animation dates back to the use of earlier techniques, but current-day video production companies specializing in animation are more dynamic and versatile.
The Final Word
Flash animation has revolutionized the digital world, making animated content accessible on the web when this type of media was previously uncommon. It transformed the way we experience web content, introducing online cartoons, banner ads, and interactive games that formed the basis of the contemporary multimedia experience we have today. Although it has been phased out, its impact cannot be ignored. Learning the history of Flash and what it represented, we are grateful that it has paved the way for HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScript to become the new stars of web animation.
Flash is a widely recognized book in the history of digital animation, remembered for its impact on creative expression through the internet. Based on the techniques, ideas, and inspiration of Flash, it has helped and continues to influence the evolution of digital animation tools, ensuring its legacy will survive in the new world of multimedia and interactive content.